Have you ever wondered what makes up the intricate world around us? From the vibrant colors of a flower to the intricate workings of our own bodies, everything is built upon the fundamental building blocks of life: cells. Understanding cells is like holding the key to unlocking the secrets of life itself. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the fascinating world of cells, exploring their structure, function, and the importance of knowing them.
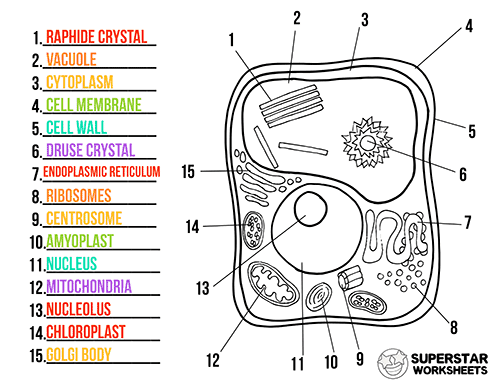
Image: mungfali.com
Imagine looking through a powerful microscope, witnessing a miniature world teeming with life. These tiny units, called cells, are the foundation of all living organisms, from the smallest bacteria to the largest whale. They carry out the essential processes that sustain life, like producing energy, replicating themselves, and communicating with other cells. As we embark on this journey of discovery, you’ll gain a deeper understanding of these microscopic marvels, which are the key to understanding the complexity and beauty of life.
The Importance of Understanding Cells
Understanding cells is crucial for unlocking the mysteries of life and advancing scientific knowledge. Studying cells helps us comprehend the fundamental processes that keep us alive, from how our bodies digest food to how our brains process information. This knowledge also forms the basis of many scientific fields, including medicine, biology, and genetics.
By delving into the world of cells, we can gain a deeper understanding of diseases, develop new treatments, and even engineer solutions for challenges like climate change and food security.
Exploring the World of Cells
Cells are the fundamental units of life, and their discovery revolutionized our understanding of biology. The invention of the microscope in the 17th century allowed scientists to observe these microscopic structures for the first time.
Cells are broadly categorized into two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells, like bacteria and archaea, are simpler in structure, lacking a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists, are more complex and possess a nucleus that houses their genetic material, along with other specialized compartments.
Understanding the structure of a cell is essential for comprehending its function. The cell membrane acts as a barrier, controlling what enters and leaves the cell. The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance that fills the cell, providing a medium for various biochemical reactions to occur. The nucleus houses the cell’s genetic material, DNA, which contains the instructions for building and maintaining the cell. The mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, generating energy through cellular respiration.
The cell’s internal structures, known as organelles, work together in a coordinated manner to sustain life. Just like different departments in a factory, each organelle contributes to a specific function, allowing the cell to perform its essential tasks.
Cells are constantly communicating with each other through various signaling mechanisms. These interactions allow cells to coordinate their activities, form tissues and organs, and respond to external stimuli. Understanding these complex interactions is crucial for understanding how organisms develop, grow, and maintain their functions.
The Power of Cell Worksheets
Cell worksheets are valuable tools for learning about the structure and function of cells. These interactive exercises engage students in a hands-on learning experience, helping them visualize and understand complex cellular concepts. Worksheets often feature diagrams, labeling exercises, fill-in-the-blank questions, and problem-solving activities, providing a comprehensive approach to learning.
By working through cell worksheets, students can reinforce their understanding of key concepts, develop critical thinking skills, and apply their knowledge in practical contexts.

Image: printableschoolschulths.z19.web.core.windows.net
Expert Tips for Mastering Cell Worksheets
Mastering cell worksheets can be a rewarding experience, unlocking a deeper understanding of cell biology. Here are some expert tips to help you excel:
- Start with the Basics: Before tackling complex worksheets, make sure you have a solid understanding of the fundamental concepts of cell biology. Review basic definitions, structures, and functions of key organelles.
- Visualize the Concepts: Use diagrams, models, or online resources to visualize cell structures and their functions. This will help you create a mental picture that reinforces your understanding.
- Practice, Practice, Practice: Working through a variety of cell worksheets will expose you to different formats, question types, and challenging concepts. Repetition and practice are key to mastering any subject.
- Seek Help When Needed: Don’t hesitate to ask your teacher, classmates, or online resources for help if you encounter any difficulties. Learning is a collaborative process, and seeking support is a sign of strength.
- Connect to Real-World Applications: Relate cell biology concepts to real-world applications like medicine, agriculture, or environmental science. Understanding the relevance of your learning will make it more engaging and memorable.
FAQ: Introduction to Cells
Here are some frequently asked questions about cells, along with clear and concise answers:
What is the smallest unit of life?
The smallest unit of life is a cell. Cells are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms, from the simplest bacteria to the most complex plants and animals.
What is the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells are simpler in structure, lacking a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells are more complex and possess a nucleus that houses their genetic material, along with other specialized compartments.
What is the function of the cell nucleus?
The nucleus is the control center of the cell. It houses the cell’s genetic material, DNA, which contains the instructions for building and maintaining the cell.
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell, controlling what enters and leaves the cell. It acts as a gatekeeper, regulating the flow of substances in and out of the cell and protecting the cell’s internal environment.
How do cells communicate with each other?
Cells communicate with each other through various signaling mechanisms, including chemical messengers, electrical signals, and direct contact. These interactions allow cells to coordinate their activities, form tissues and organs, and respond to external stimuli.
Introduction To Cells Worksheet Answer Key
Conclusion
Understanding cells is essential for unlocking the mysteries of life and advancing scientific knowledge. Cell worksheets are valuable tools for learning about the structure and function of cells, providing a hands-on learning experience that engages students in a deeper level of understanding. By working through these interactive exercises, you can develop a strong foundation in cell biology and explore the fascinating world of these microscopic structures.
Are you interested in learning more about cells and their role in life? Share your thoughts in the comments below!



![Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF] Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF]](https://i3.wp.com/i.ebayimg.com/images/g/2OEAAOSwxehiulu5/s-l1600.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)

