Imagine a symphony conducted by your brain, with your muscles acting as the instruments and your joints as the conductor. Each joint, with its unique range of motion, contributes to a harmonious blend of movement, enabling us to navigate the world with grace and purpose.
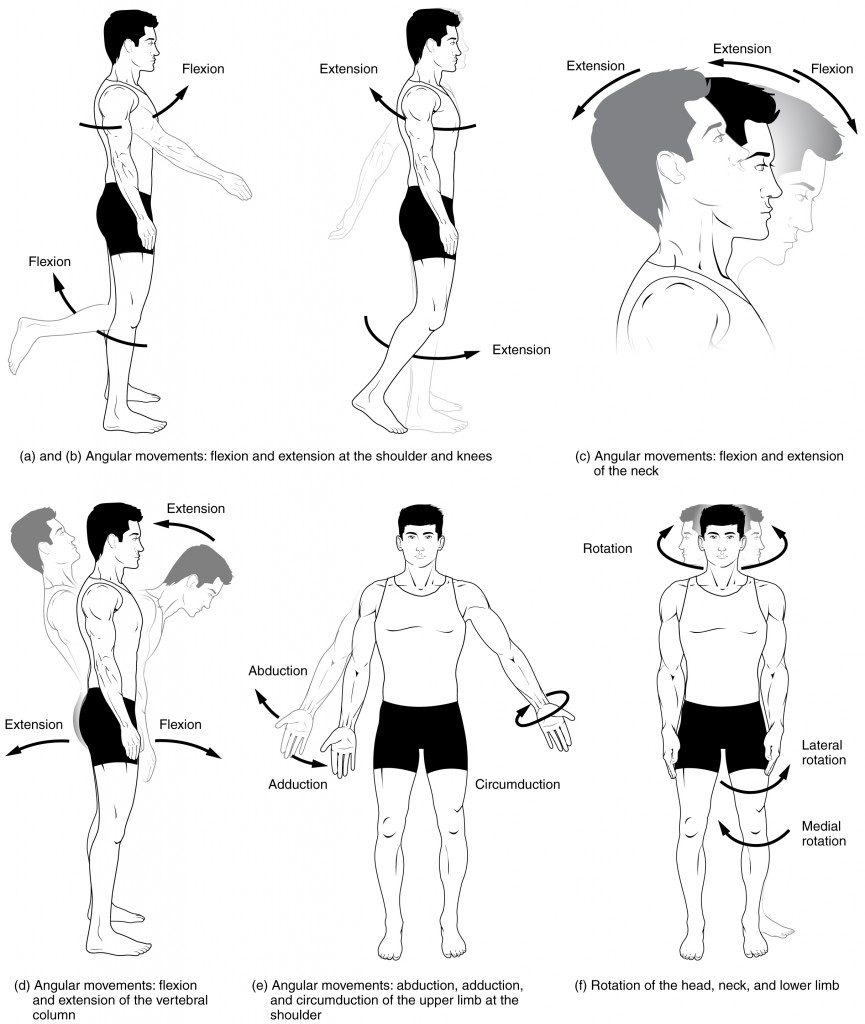
Image: www.blendspace.com
This article delves into the fascinating realm of human movement, exploring the critical role of 10 key joints in our everyday activities. We’ll uncover how these joints work together to facilitate a vast array of complex motions, from the simple act of walking to the intricate choreography of running, swimming, and dancing. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting your fitness journey, understanding how your joints function and how to exercise them appropriately is crucial for optimal health and performance.
Understanding Joint Movement
Joints are the meeting points of two or more bones, acting as the hinges and pivots that allow our bodies to move. The type of joint determines the range of motion it can achieve. For instance, the hinge joint of the elbow allows for flexion and extension, while the ball-and-socket joint of the hip permits movement in all directions.
To master exercise for 10 key joints and body movements, we’ll examine these in depth:
1. Shoulder Joint
Movement:
- Flexion: Raising the arm forward
- Extension: Bringing the arm backward
- Abduction: Lifting the arm away from the body
- Adduction: Bringing the arm toward the body
- Internal Rotation: Rotating the arm inward
- External Rotation: Rotating the arm outward
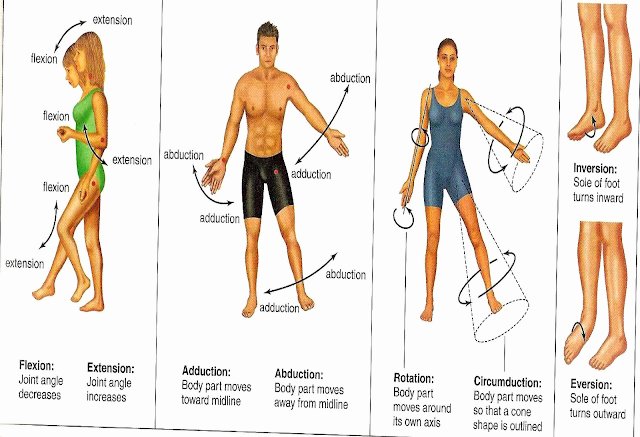
Image: imsyaf.com
Exercises:
- Overhead Press: Targets shoulder flexion and extension, as well as triceps strength.
- Lateral Raises: Isolates shoulder abduction, strengthening the deltoid muscles.
- Front Raises: Engage shoulder flexion and the front deltoid muscles.
2. Elbow Joint
Movement:
- Flexion: Bending the elbow
- Extension: Straightening the elbow
Exercises:
- Bicep Curls: Focus on elbow flexion and biceps strength.
- Triceps Extensions: Engage elbow extension and triceps muscles.
3. Wrist Joint
Movement:
- Flexion: Bending the wrist upward
- Extension: Bending the wrist downward
- Radial Deviation: Moving the wrist toward the thumb side
- Ulnar Deviation: Moving the wrist toward the pinky side
Exercises:
- Wrist Curls: Target wrist flexion and flexor muscles.
- Reverse Wrist Curls: Strengthen wrist extension and extensor muscles.
4. Hip Joint
Movement:
- Flexion: Bringing the thigh toward the abdomen
- Extension: Straightening the leg behind the body
- Abduction: Moving the leg away from the midline
- Adduction: Moving the leg toward the midline
- Internal Rotation: Rotating the leg inward
- External Rotation: Rotating the leg outward
Exercises:
- Lunges: Engage hip flexion, extension, and core strength.
- Squats: Work the hip flexors, extensors, and gluteal muscles.
- Hip Abductions: Strengthen hip abduction and the gluteus medius muscle.
5. Knee Joint
Movement:
- Flexion: Bending the knee
- Extension: Straightening the knee
Exercises:
- Leg Extensions: Isolate knee extension and quadricep strength.
- Hamstring Curls: Strengthen knee flexion and hamstring muscles.
6. Ankle Joint
Movement:
- Dorsiflexion: Pointing the toes upward
- Plantarflexion: Pointing the toes downward
- Inversion: Lifting the arch of the foot inward
- Eversion: Lifting the arch of the foot outward
Exercises:
- Calf Raises: Strengthen plantarflexion and calf muscles.
- Toe Curls: Work the intrinsic muscles of the foot, enhancing stability and balance.
7. Jaw Joint (Temporomandibular Joint)
Movement
- Elevation: Closing the jaw
- Depression: Opening the jaw
- Protrusion: Moving the jaw forward
- Retrusion: Moving the jaw backward
- Lateral Excursion: Moving the jaw to the side
Exercises
- Jaw Clenching: Tense and relax the jaw muscles.
- Jaw Opening and Closing: Practice controlled jaw movements.
8. Vertebral Joints
Movement:
- Flexion: Bending forward
- Extension: Bending backward
- Lateral Flexion: Bending to the side
- Rotation: Twisting the torso
Exercises:
- Plank: Engages core muscles and improves spinal stability.
- Bird Dog: Strengthens back muscles and promotes core engagement.
9. Thumb Joint (Carpometacarpal Joint)
Movement
- Flexion: Bending the thumb toward the palm
- Extension: Straightening the thumb
- Abduction: Moving the thumb away from the palm
- Adduction: Moving the thumb toward the palm
- Opposition: Touching the thumb to the fingertips
Exercises:
- Thumb Extensions: Strengthen the thumb extensor muscles.
- Thumb Abductions: Engage thumb abduction and surrounding hand muscles.
- Pinch Grips: Improve grip strength and coordination.
10. Finger Joints (Metacarpophalangeal and Interphalangeal Joints)
Movement:
- Flexion: Bending the finger
- Extension: Straightening the finger
Exercises:
- Finger Curls: Strengthen finger flexion and flexor muscles.
- Finger Extensions: Work finger extension and extensor muscles.
The Importance of Joint Movement and Exercise
Regular exercise tailored to improve joint movement is essential for a multitude of reasons:
- Increased Range of Motion: Exercise helps maintain or improve the flexibility and mobility of your joints, preventing stiffness and discomfort.
- Strength and Stability: Strengthening the muscles surrounding the joints provides support and stability, reducing the risk of injuries.
- Pain Management: Exercise can alleviate pain caused by arthritis, osteoporosis, and other conditions by improving joint function and reducing inflammation.
- Improved Balance and Coordination: Exercising a variety of joint movements enhances balance and coordination, making everyday activities easier and reducing the risk of falls.
- Enhanced Overall Health: Regular exercise promotes cardiovascular health, reduces stress levels, and improves sleep quality, leading to a better quality of life.
Tips for Safe and Effective Joint Exercise
To maximize the benefits of joint exercise and minimize the risk of injury, follow these guidelines:
- Warm Up Properly: Before starting any exercise routine, warm up your muscles with light cardio and dynamic stretching to prepare them for the workout.
- Start Slowly and Gradually Increase Intensity: Avoid overexertion, especially when starting a new exercise program. Begin with manageable amounts of repetitions and weight and progressively increase as you gain strength and flexibility.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any pain or discomfort and stop the exercise if necessary. If you experience persistent pain, consult with a healthcare professional.
- Use Proper Form: Incorrect form can put undue stress on your joints and lead to injury. Focus on maintaining good posture and technique throughout your exercises.
- Include Variety: Incorporate various types of exercises targeting different muscle groups and joint movements to ensure well-rounded development and reduce the risk of overuse injuries.
Exercise 10 Joints And Body Movements
Conclusion
Understanding the role of your 10 key joints and incorporating targeted exercises into your routine is a powerful step toward achieving optimal physical health. By listening to your body, practicing safe technique, and progressively challenging yourself, you can unlock the full potential of your joints, experience a wider range of movements, and live a more active, fulfilling life. So, get moving, explore the possibilities, and discover the joy of a well-tuned body, where every move is a symphony of motion!



![Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF] Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF]](https://i3.wp.com/i.ebayimg.com/images/g/2OEAAOSwxehiulu5/s-l1600.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)

