Imagine stepping into a bustling marketplace, filled with traders shouting bids and offers, the air thick with the scent of money and opportunity. Amidst the chaos, you spot an intriguing pattern emerging – a subtle dance of prices that whispers secrets about the market’s hidden intentions. This is the world of candlestick charts, a visual dialect that reveals the ebb and flow of supply and demand, offering valuable clues for day traders.
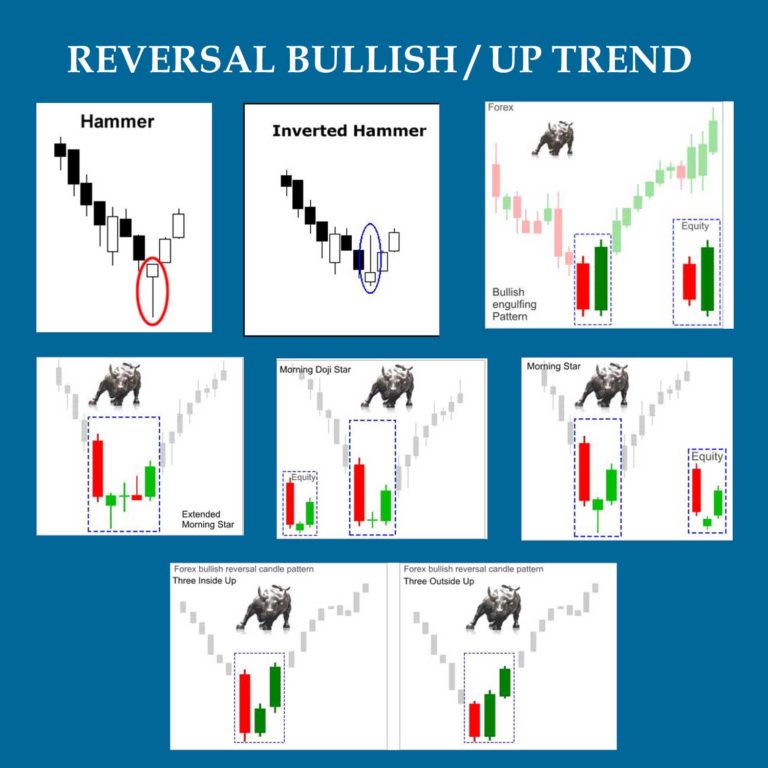
Image: www.aiophotoz.com
In the realm of day trading, where fortunes can be made and lost in the blink of an eye, understanding the language of candlestick charts is paramount. These charts, with their unique visual representation of price fluctuations, provide a powerful tool for deciphering market sentiment and identifying potential trading opportunities. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and skills to navigate the complexities of candlestick patterns, enabling you to gain a competitive edge in the fast-paced world of day trading.
The Fundamentals of Candlestick Charts
Unlike traditional bar charts, which simply display the high, low, open, and close prices of an asset, candlestick charts delve deeper into the market’s dynamics by adding a visual element to price movements. Each candlestick represents a specific time period, typically a minute, hour, or day, and encapsulates the price action within that timeframe.
Deciphering the Anatomy of a Candlestick
Each candlestick comprises four key components:
- Body: The body represents the difference between the opening and closing price of the asset during the time period.
- Upper Shadow: The upper shadow, also known as the wick, extends from the body’s top to the highest price reached during the period.
- Lower Shadow: The lower shadow, or wick, extends from the body’s bottom to the lowest price reached during the period.
- Color: Candlesticks typically use color to differentiate between bullish and bearish price movements. Green or white candles indicate a closing price higher than the opening price (bullish), while red or black candles depict a closing price lower than the opening price (bearish).
The Power of Patterns: Recognizing Candlestick Formations
The true beauty of candlestick charts lies in their ability to reveal complex market patterns. These patterns, or formations, arise from the interplay of buyers and sellers, providing valuable insights into the prevailing market sentiment and potential future price movements. Mastering these patterns is like learning a new language, enabling you to decipher the market’s hidden messages.

Image: www.pinterest.com
Popular Candlestick Patterns for Day Traders
Here are some popular and effective candlestick patterns frequently used by day traders:
- Bullish Engulfing Pattern: This pattern suggests a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend. It consists of a small red or black candlestick followed by a large green or white candlestick that fully engulfs the body of the previous candle.
- Bearish Engulfing Pattern: This pattern signals a potential downtrend reversal. It comprises a small green or white candlestick followed by a large red or black candlestick that completely engulfs the body of the previous candle.
- Morning Star Pattern: This bullish pattern indicates a potential reversal from a downtrend. It consists of three candlesticks: a small red or black candle, a small green or white candle (the “star”), and a large green or white candle that closes above the midpoint of the first candle.
- Evening Star Pattern: This bearish pattern signals a potential reversal from an uptrend. It comprises three candlesticks: a small green or white candle, a small red or black candle (the “star”), and a large red or black candle that closes below the midpoint of the first candle.
- Hammer Pattern: This bullish pattern suggests a potential bottom reversal. It features a small body with a long lower shadow and a tiny upper shadow.
- Hanging Man Pattern: This bearish pattern signals a potential top reversal. It includes a small body with a long lower shadow and a tiny upper shadow, similar to the hammer pattern but appears at the top of an uptrend.
- Shooting Star Pattern: This bearish pattern suggests a potential top reversal. It features a small body with a long upper shadow and a tiny lower shadow.
- Doji Pattern: This pattern signifies indecision in the market, with the open and close prices being almost identical. Doji candlesticks have very short bodies and long upper and lower shadows, signaling a potential stalemate between buyers and sellers.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Candlestick Techniques
While mastering basic candlestick patterns is essential for day traders, delving into advanced techniques can further enhance your trading skills. These techniques involve combining candlestick patterns with other indicators to gain a more comprehensive understanding of market dynamics.
Combining Candlestick Patterns with Technical Indicators
Technical indicators are mathematical formulas that analyze price data and provide additional insights into market trends. Combining these indicators with candlestick patterns can provide a more robust and reliable trading strategy. Popular technical indicators used in conjunction with candlestick patterns include:
- Moving Averages: Moving averages smooth out price fluctuations and help identify trends. Traders often use moving averages to confirm candlestick signals and identify support and resistance levels.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI is a momentum indicator that measures the strength of price movements. Combining the RSI with candlestick patterns can help traders assess whether a trend is overbought or oversold.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): The MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that helps traders identify potential trend changes, confirming or contradicting candlestick signals.
Understanding Volume and Its Importance
Volume plays a crucial role in interpreting candlestick patterns. It represents the number of shares or contracts traded during a specific period and provides insight into the strength of market movements. High volume signals strong buyer or seller conviction, while low volume suggests weaker interest in the asset.
For instance, if a bullish engulfing pattern emerges on high volume, it indicates a strong buying pressure and a more reliable likelihood of an uptrend reversal. Conversely, if the same pattern appears on low volume, it might signal a weak buying pressure, making the reversal less reliable.
Practical Applications: Using Candlestick Charts in Day Trading
Understanding candlestick patterns and their interplay with technical indicators is vital for making informed trading decisions. Here are some practical applications of this knowledge in day trading:
Identifying Entry and Exit Points
Candlestick patterns can help traders pinpoint optimal entry and exit points. For example, spotting a bullish engulfing pattern on high volume indicates a potential entry point for buying an asset, while a bearish engulfing pattern on high volume suggests a potential exit point for selling.
Gauging Market Sentiment and Trend Reversals
Candlestick patterns provide valuable information about market sentiment and potential trend reversals. For instance, a morning star pattern might indicate a reversal from a downtrend, while a shooting star pattern suggests a potential top reversal.
Managing Risk and Stop-Loss Orders
Combining candlestick patterns with stop-loss orders can help manage risk effectively. For example, placing a stop-loss order below a potential support level identified through candlestick patterns can limit potential losses if the market moves against the trader’s position.
The Importance of Practice and Discipline
Mastering the art of reading candlestick charts requires consistent practice and disciplined application. Don’t be discouraged by the initial learning curve; start with basic patterns and gradually move towards advanced techniques. Analyze historical price data, experiment with different scenarios, and continuously refine your trading strategy.
Remember, practice makes perfect. The more time you dedicate to studying and applying candlestick patterns, the better equipped you will be to navigate the complexities of the market, make informed trading decisions, and ultimately achieve success in the exciting world of day trading.
How To Read Candlestick Chart For Day Trading Pdf
Conclusion
Candlestick charts, with their rich tapestry of patterns and insights, offer a powerful tool for any day trader seeking to decipher the market’s language and make informed trading decisions. By mastering the fundamentals and exploring advanced techniques, you gain a competitive advantage, unlocking the potential for profit in the dynamic world of day trading. Remember, continuous learning, disciplined practice, and a well-defined trading strategy are crucial for navigating the fluctuating tides of the market and achieving consistent success.



![Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF] Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF]](https://i3.wp.com/i.ebayimg.com/images/g/2OEAAOSwxehiulu5/s-l1600.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)

