Have you ever wondered what makes up all living things, from the smallest bacteria to the tallest trees? The answer lies within the fascinating world of cells, the fundamental building blocks of life. These tiny structures are incredibly complex and diverse, each playing a critical role in the functioning of organisms. Understanding the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is crucial for grasping the intricate workings of life itself.

Image: gustavogargiulo.com
This guide will help you navigate the intricacies of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells through the lens of worksheets, those invaluable tools for learning and reinforcing knowledge. We’ll journey through a comprehensive exploration of these cellular types, uncovering their unique features, functions, and the importance of understanding their differences.
Understanding the Building Blocks of Life: Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
The world of cells is vast and intricate, with numerous types of cells making up the diverse tapestry of life. However, for our purposes, we will focus on the two major categories: prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Let’s start with the basics:
-
Prokaryotic cells are simple and ancient, lacking a nucleus and many other membrane-bound organelles. They are essentially the “minimal” cell structure, found in single-celled organisms like bacteria and archaea. These cells are often smaller than eukaryotic cells and have a simpler internal structure.
-
Eukaryotic cells are more complex and evolved, containing a true nucleus that houses their genetic material. They possess a vast array of organelles, each specializing in a specific function. Eukaryotic cells are found in all multicellular organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and protists.
Exploring the Key Differences: A Worksheet Perspective
To fully grasp the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, it’s essential to understand their unique structures and functions. Let’s break down the key distinctions:
1. Nucleus: The Control Center
- Prokaryotic cells: They lack a membrane-bound nucleus; their DNA is located in a region called the nucleoid, which is not separated from the rest of the cell.
- Eukaryotic cells: They possess a well-defined, membrane-bound nucleus where their genetic material (DNA) is organized and protected.
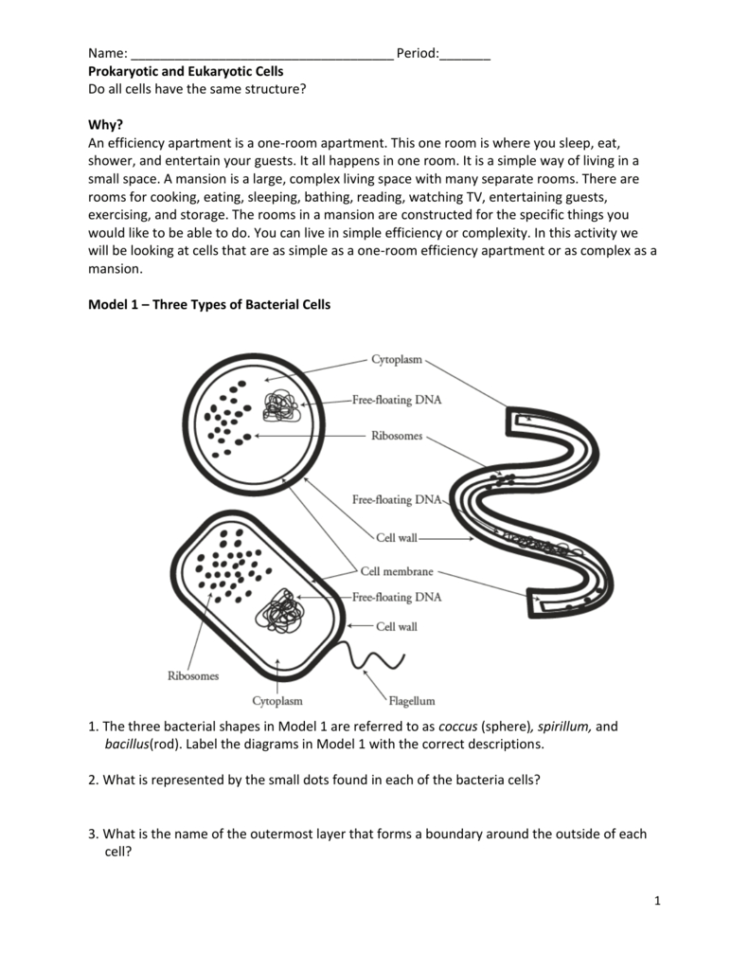
Image: printablefullchiff.z19.web.core.windows.net
2. Organelles: Specialized Workplaces
- Prokaryotic cells: They have limited internal membrane structures, most notably ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis. The absence of other organelles implies a simpler cellular organization.
- Eukaryotic cells: They boast an array of specialized organelles, each with a specific function. These include:
- Mitochondria: The powerhouse of the cell, responsible for energy production.
- Endoplasmic reticulum: A network of membranes involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
- Golgi apparatus: Processes and packages proteins for delivery.
- Lysosomes: Act as the cell’s recycling center.
3. Cell Wall: Structural Support
- Prokaryotic cells: Many prokaryotes possess a rigid cell wall made of peptidoglycan, providing them with structural support and protection.
- Eukaryotic cells: In plants and fungi, a cell wall provides structural support, but its composition differs from that of prokaryotic cells. Animal cells do not have a cell wall.
4. Size: A Matter of Scale
- Prokaryotic cells: Typically smaller, ranging from 0.1 to 10 micrometers in diameter.
- Eukaryotic cells: Generally larger, usually 10 to 100 micrometers in diameter.
Applying Worksheet Principles for Enhanced Understanding
Worksheets are effective learning tools that provide a structured framework for understanding complex concepts. Here’s how they can be applied to the study of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells:
- Visual diagrams: Worksheets often present labelled diagrams of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, highlighting their key structures and differences.
- Labeling exercises: This requires students to correctly identify different organelles and structures within each cell type, reinforcing their understanding of their location and function.
- Comparative analysis: Many worksheets use tables or charts to compare and contrast the characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, making it easier to identify their unique features.
- Real-world applications: Some worksheets may include scenarios or questions that link the concepts to real-world applications. For example, discussing the role of antibiotics in targeting prokaryotic cells or the importance of eukaryotic cells in multicellular organisms.
Using Worksheets to Craft a Deeper Understanding
By engaging with worksheets, students can actively learn and retain information about prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. This approach promotes:
- Active recall: Completing exercises and answering questions requires students to actively retrieve and recall information, strengthening their learning.
- Visual learning: Diagrams and illustrations provide a visual representation of cell structures, aiding in comprehension and memory retention.
- Critical thinking: Worksheets often include thought-provoking questions that encourage students to analyze, synthesize, and interpret information.
- Hands-on experience: Engaging with worksheets allows students to experience the learning process in a practical way, enhancing their understanding of cell biology.
Beyond the Worksheet: Applications in the Real World
Understanding the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells has numerous practical applications in various fields:
- Medicine: The study of prokaryotic cells, particularly bacteria, is essential for understanding infectious diseases and developing new antibiotics.
- Agriculture: Prokaryotes play a vital role in soil fertility and nutrient cycling, shaping agricultural practices.
- Biotechnology: Research on both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is critical for developing new drugs, gene therapy, and other biotechnological advancements.
Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet Answer Key
Conclusion: Embracing the Journey of Cell Discovery
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are the fundamental units of life, each with its own unique characteristics and contributions. Understanding their differences is crucial for grasping the intricacies of biology and exploring the vast diversity of life on Earth. Worksheets offer a valuable tool for learning and reinforcing these essential concepts. By engaging with them, students can embark on a journey of discovery, unlocking the secrets of these remarkable cellular worlds. Remember, the exploration of cells is a continuous journey, and this guide serves as a stepping stone to a deeper understanding of the incredible complexities of the living world.



![Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF] Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF]](https://i3.wp.com/i.ebayimg.com/images/g/2OEAAOSwxehiulu5/s-l1600.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)

