Have you ever wondered what makes up the objects around us? Everything we see, touch, and experience is composed of tiny, invisible building blocks called atoms. But atoms aren’t always content to exist alone. Sometimes they shed or gain electrons, leading to the formation of charged entities known as ions. Understanding the difference between atoms and ions is crucial for comprehending the fundamental building blocks of nature and the chemical reactions that drive the world around us.

Image: www.pdffiller.com
This article will serve as your comprehensive guide to deciphering the mysteries of atoms and ions. We’ll delve into their core concepts, explore their fascinating properties, and uncover how they interact with each other to create diverse molecules and compounds. Get ready to embark on an exciting journey through the realm of chemistry!
Unveiling the Atom: The Foundation of Matter
At the heart of chemistry lies the atom, the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Picture a miniature solar system with a dense, positively charged nucleus at the center, orbited by negatively charged electrons in a cloud-like distribution. This model, while simplified, captures the essence of the atom’s structure.
- The Nucleus: Composed of protons and neutrons, the nucleus accounts for most of the atom’s mass. Protons carry a positive charge, while neutrons are neutral, contributing to the atom’s stability.
- Electrons: Whizzing around the nucleus in specific energy levels, electrons carry a negative charge and are responsible for chemical bonding.
- Atomic Number: An atom’s identity is determined by its atomic number, the number of protons in its nucleus. For instance, all carbon atoms have six protons, defining their unique atomic number.
Transformations: When Atoms Become Ions
While atoms are generally neutral, carrying an equal number of protons and electrons, they can gain or lose electrons in a process known as ionization. This transformation leads to the formation of ions, atoms with a net electrical charge.
- Cations: Atoms that lose electrons acquire a positive charge and are known as cations. For example, sodium (Na) readily loses one electron to become a sodium ion (Na+).
- Anions: Atoms that gain electrons acquire a negative charge and are known as anions. For instance, chlorine (Cl) readily gains one electron to become a chloride ion (Cl-).
Exploring the Realm of Ions: A World of Reactivity
Ions, unlike neutral atoms, have a strong tendency to interact with other ions or polar molecules. These interactions are driven by electrostatic forces, where opposite charges attract, leading to the formation of ionic bonds.
- Ionic Compounds: These compounds are formed by the electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions. A classic example is table salt (NaCl), formed by the electrostatic interaction between sodium cations (Na+) and chloride anions (Cl-).
- Ionic Bonding: The force of attraction between oppositely charged ions is known as ionic bonding. These bonds are typically strong, contributing to the stability of ionic compounds.
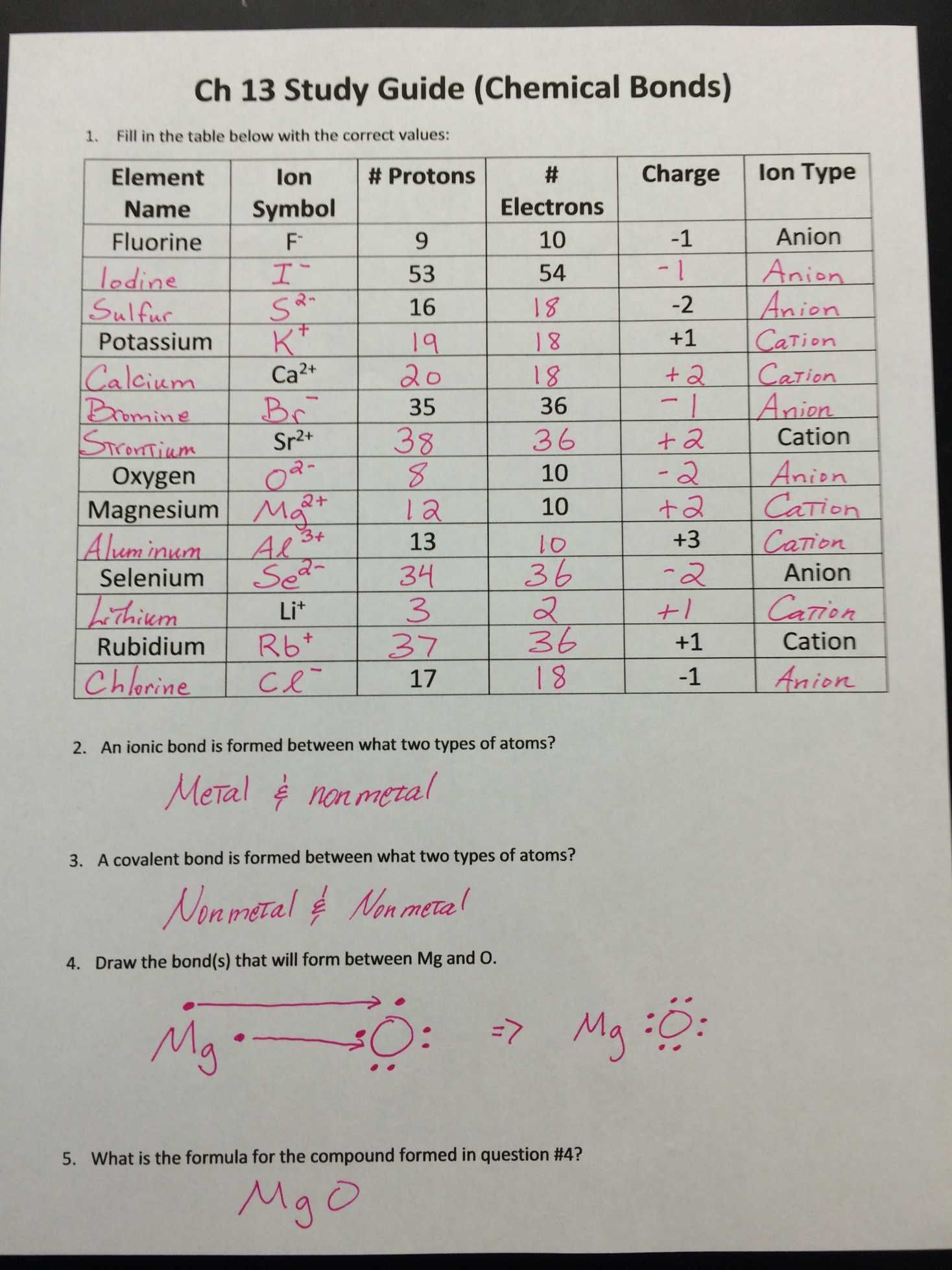
Image: db-excel.com
Applications of Atoms and Ions: From Medicine to Technology
The study of atoms and ions is not confined to textbooks; it plays a crucial role in shaping our world and profoundly affects our daily lives.
- Medical Applications: Radioactive isotopes, atoms with unstable nuclei, are used in medical imaging techniques, such as PET scans, and cancer therapy using radiation.
- Technological Advancements: Semiconductors, crucial components in electronic devices, leverage the unique electrical conductivity properties of different atoms and ions.
- Environmental Science: Ion exchange is used in water treatment processes to remove pollutants and soften hard water.
Atoms vs. Ions Worksheet: A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding Matter
A well-structured atoms vs. ions worksheet provides a valuable tool for reinforcing key concepts and fostering a deeper understanding of these fundamental building blocks of matter. Here’s how a typical worksheet might be structured:
- Introduction: The worksheet might begin with a brief overview of atoms and ions, defining key terms like atomic number, mass number, and the difference between cations and anions.
- Multiple Choice Questions: Multiple choice questions can assess understanding of basic concepts and encourage critical thinking skills. For example, “Which of the following is a cation? A. Cl- B. O2- C. Na+ D. N3- “.
- Matching Scenarios: Matching scenarios can help students connect the concepts of atoms and ions with real-world examples. For example, “Match the following atoms with their corresponding ions: A. Sodium (Na) B. Chlorine (Cl) C. Oxygen (O) D. Magnesium (Mg) 1. Mg2+ 2. Na+ 3. Cl- 4. O2- “.
- True/False Statements: True/False statements challenge students to identify the accuracy of various claims related to atoms and ions. For example, “All atoms have the same number of protons and electrons.”
- Fill-in-the-Blanks: Fill-in-the-blanks questions encourage students to recall and apply memorized information. For example, “When a chlorine atom gains an electron, it becomes a ___ ion.”
- Short Answer Questions: Short answer questions allow students to express their understanding in their own words. For example, “Explain the difference between an atom and an ion.”
- Diagram Interpretation: Diagrams of atoms and ions can be presented, asking students to label components like the nucleus, protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Atoms Vs Ions Worksheet Answers Key
https://youtube.com/watch?v=SojtC0lWE10
Unlocking the Secrets of Atoms vs. Ions: A Journey of Exploration
Working through an atoms vs. ions worksheet can be an engaging and rewarding journey of discovery. By diving into the intricacies of these tiny building blocks, you gain a deeper appreciation for the complex world around us. We’ve explored the fundamental concepts of atoms and ions, delved into their fascinating properties, and highlighted their diverse applications in various fields.
Armed with this knowledge, you can explore further resources, conduct independent research, and even experiment with basic chemistry concepts at home. Remember, the world of chemistry is vast and filled with wonders waiting to be uncovered. So, keep exploring, keep asking questions, and keep unlocking the secrets of matter!



![Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF] Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF]](https://i3.wp.com/i.ebayimg.com/images/g/2OEAAOSwxehiulu5/s-l1600.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)

