Ever wondered what makes bread rise, yogurt tangy, and your stomach rumble? It’s the microscopic world of microbes! These tiny organisms are everywhere, playing critical roles in our lives, from food production to environmental health. In the Science Olympiad’s Microbe Mission event, you’ll dive into this fascinating world, exploring microbial growth, identification, and applications. This cheat sheet will equip you with the knowledge and strategies needed to excel in this event.
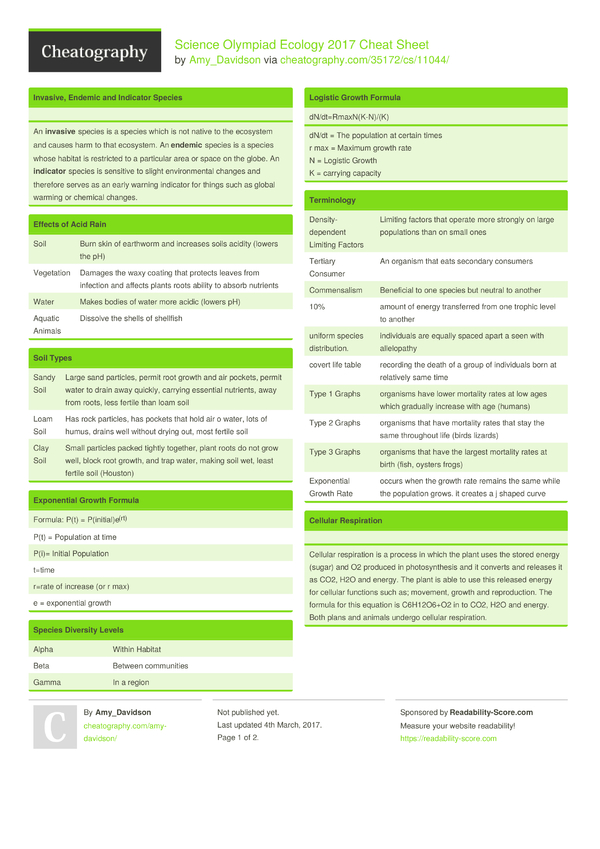
Image: mavink.com
The Microbe Mission event tests your understanding of microbiology, a field that explores the fascinating world of bacteria, fungi, viruses, protozoa, and algae. This event is more than just memorizing facts; it’s about applying scientific principles to solve real-world challenges related to microbes. Think of it as a scientific detective game, uncovering the secrets of these tiny organisms and their impact on our world.
Understanding the Basics: Building a Microbial Foundation
To navigate the Microbe Mission, you need a solid foundation in microbiology. Here are some essential concepts:
1. Microbial Diversity: A World of Wonders
Microbes come in all shapes and sizes, each with unique characteristics.
- Bacteria: Single-celled prokaryotes, incredibly diverse in their metabolism and habitat preferences. Some are beneficial (e.g., gut bacteria), while others can cause disease.
- Fungi: Eukaryotic organisms, including molds, yeasts, and mushrooms. They play crucial roles in decomposition and food production.
- Viruses: Non-living particles, requiring a host cell to replicate. Some viruses cause disease, while others are used in biotechnology.
- Protozoa: Single-celled eukaryotic organisms, found in diverse environments. Some are parasites, while others are free-living.
- Algae: Photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms, ranging from single-celled diatoms to giant kelp. They are primary producers in aquatic ecosystems.
2. Microbial Growth: From Single to Millions
Microbes multiply rapidly through a process called binary fission, where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Factors influencing microbial growth include:
- Temperature: Each microbe has an optimal temperature range for growth.
- pH: The acidity or alkalinity of the environment affects microbial growth.
- Nutrients: Microbes require specific nutrients for growth, such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus.
- Oxygen: Some microbes require oxygen (aerobic), while others cannot tolerate it (anaerobic).

Image: www.scribd.com
3. Microbial Identification: Unmasking the Unknown
Identifying microbes is crucial for understanding their role in different environments. Common identification methods include:
- Microscopy: Observing microbes under a microscope, revealing their morphology (shape, size, arrangement).
- Staining: Using dyes to visualize different structures within microbes.
- Culture Techniques: Growing microbes on specific media to observe their growth characteristics and appearance.
- Biochemical Tests: Analyzing microbial metabolism to identify their unique enzymatic activities.
- Molecular Techniques: DNA sequencing and PCR, allowing for more precise identification and studying genetic diversity.
Key Skills for Success: Navigating the Microbe Mission
The Microbe Mission requires a blend of knowledge and hands-on skills. Here are some key skills to master:
1. Aseptic Technique: Preventing Contamination
Aseptic technique is essential to prevent contamination during microbial experiments. Key principles include:
- Sterilizing equipment: Using heat, chemicals, or filtration to eliminate microbes from surfaces and solutions.
- Using sterile media: Avoiding introducing unwanted microbes to growth media.
- Working in a sterile environment: Minimizing the possibility of airborne contamination.
- Proper hand washing: Washing hands thoroughly before and after handling microbes.
2. Culturing Microbes: Growing Your Microbial Friends
Growing microbes in a laboratory setting enables their study and identification.
- Preparation of Culture Media: Formulating media that provides nutrients required for specific microbial growth (e.g., agar, nutrient broth).
- Streaking Techniques: Aseptic techniques for evenly spreading microbes onto agar plates, allowing for colony isolation.
- Incubation Conditions: Ensuring optimal temperature and atmosphere for microbial growth.
- Observation and Interpretation: Observing microbial growth characteristics such as colony morphology, color, and size.
3. Microbial Applications: Putting Knowledge to Work
The world of microbes is not just about disease; it’s also about beneficial applications.
- Food Production: Microbes are essential for fermenting food, producing yogurt, cheese, bread, and other fermented products.
- Biotechnology: Microbes are used in the production of pharmaceuticals, enzymes, biofuels, and other products.
- Bioremediation: Microbes help clean up pollution, breaking down pollutants into less harmful substances.
- Agriculture: Microbes improve soil health, promote plant growth, and protect crops from disease.
Tips and Strategies for Success: Mastering the Microbe Mission
Preparing for the Microbe Mission requires more than just reading textbooks. It’s about actively engaging with the material and sharpening your skills. Here are some tips:
- Practice, Practice, Practice: Practice aseptic technique and culturing methods regularly to develop proficiency.
- Engage with Real-World Applications: Research real-world examples of how microbes are used in food production, medicine, and environmental cleanup.
- Understand the Scientific Method: Be able to design, conduct, and analyze experiments related to microbial growth and identification.
- Collaborate with your Team: Work together to brainstorm ideas, solve problems, and develop strategies for the competition.
- Stay Updated: Keep up-to-date with the latest research and developments in microbiology.
Science Olympiad Microbe Mission Cheat Sheet
Conclusion: Unleashing Your Inner Microbiologist
The Science Olympiad Microbe Mission is more than just a competition; it’s an opportunity to explore the fascinating world of microbes and their impact on our lives. By understanding their diversity, growth, identification, and applications, you can unlock a whole new perspective on the environment around you. Remember, the key to success is to approach the event with a curious mind, a willingness to learn, and a passion for unraveling the mysteries of the microbial world. So, put on your lab coat, grab your petri dishes, and let the microbes guide you!



![Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF] Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF]](https://i3.wp.com/i.ebayimg.com/images/g/2OEAAOSwxehiulu5/s-l1600.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)

