Ever wondered how your computer boots up? It’s all thanks to a small program called the BIOS, or more recently, UEFI firmware. This hidden piece of software acts as the intermediary between your hardware and your operating system, allowing your computer to function. But just like any software, the BIOS or UEFI firmware can become outdated, leading to compatibility issues, security vulnerabilities, or even performance problems. That’s where searching for and installing updates comes in.

Image: www.coursehero.com
This lab will guide you through the process of finding and updating your computer’s BIOS or UEFI firmware. This process may seem complex, but it’s essential for maintaining the optimal performance and security of your system. We’ll explore different methods of searching for updates, understanding version numbers, and the importance of careful navigation during the update process. Let’s dive into the world of BIOS or UEFI firmware updates and learn how to keep your computer running smoothly!
Introduction to BIOS and UEFI
The Foundation: BIOS
The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) is a fundamental piece of software that resides on a chip embedded on your motherboard. It’s the first program that runs when you power on your computer. The BIOS performs essential tasks like:
- Initializing the hardware: From checking if your CPU, RAM, and hard drive are working correctly to setting up basic input and output devices.
- Boot sequence: Determining the order in which your computer tries to boot from various devices, such as your hard drive, USB drive, or CD/DVD.
- Loading the operating system: Once the BIOS has successfully initialized the hardware, it loads the operating system from the configured boot device.
The Modern Update: UEFI
UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface) is a newer and more advanced firmware interface that aims to replace the traditional BIOS. UEFI offers several benefits over BIOS, including:
- Graphical interface: UEFI typically offers a graphical interface, making it easier for users to navigate and configure settings.
- Faster boot times: UEFI utilizes a faster boot process, allowing your computer to boot up significantly quicker.
- Enhanced security: UEFI introduces more robust security features, helping protect your system from malware and unauthorized access.
- Larger boot device support: UEFI supports boot devices larger than 2.2 TB, a limitation of the older BIOS.
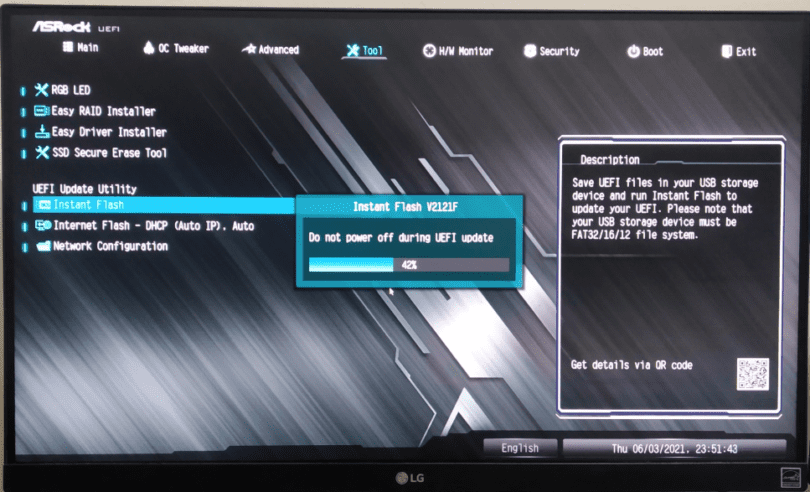
Image: linuxhint.com
Why Are Updates Needed?
Firmware updates are crucial for a few important reasons:
- Bug fixes: Developers continually improve their software, including firmware, by releasing updates that address bugs, stability issues, and performance bottlenecks.
- Security patches: As new security vulnerabilities are discovered, firmware updates are necessary to patch these vulnerabilities and prevent potential hacking attempts.
- New hardware support: As new hardware components are introduced, firmware updates may be required to ensure compatibility and optimal functionality.
- Added features: Sometimes, firmware updates can bring exciting new features and functionalities to your system.
Methods for Finding Updates
Let’s explore some of the most common methods to find updates for your computer’s BIOS or UEFI firmware:
1. Manufacturer’s Website
The most reliable source for BIOS or UEFI firmware updates is the official website of your motherboard manufacturer (e.g., ASUS, Gigabyte, MSI, etc.). Here’s how to find updates:
- Locate your motherboard model: Check the model name on your motherboard or use a system information tool like CPU-Z to find the exact model number.
- Visit the manufacturer’s support section: Go to the support or download section of the manufacturer’s website.
- Search for your motherboard model: Use the search bar or browse the support pages to locate your motherboard model.
- Download the latest firmware: Find the firmware update section and download the latest version for your motherboard, paying close attention to compatibility notes.
2. The BIOS or UEFI Setup Utility
Most modern BIOS or UEFI firmware interfaces include a built-in update feature that can directly search for and download updates. Here’s how to access the update feature:
- Access BIOS/UEFI setup: During the boot process, press the designated key (usually Del, F2, F10, or ESC) to access the BIOS or UEFI setup utility.
- Locate the update option: Look for a menu or option related to “BIOS Update,” “Firmware Update,” or “Flash BIOS.”
- Follow the instructions: The update process will usually guide you through the necessary steps, often involving downloading and installing the update from the internet or a USB drive.
3. System Information Tools
Third-party system information tools like CPU-Z or Speccy can provide details about your motherboard and its BIOS/UEFI version. While they may not directly offer update links, they can help you pinpoint the exact model and version you need to search for on the manufacturer’s website.
Important Considerations Before Updating
Updating your BIOS or UEFI firmware is not a casual procedure. It can be a complex process with potentially severe consequences if not handled correctly. Consider these crucial points before proceeding:
1. Data Backup
Before embarking on any firmware update, ensure you have a recent backup of your important data. This is crucial because a failed update could potentially corrupt your hard drive, leading to data loss. A full system backup is a wise precaution.
2. Power Source
Avoid interrupting the update process while it’s underway. Ensure your computer is connected to a stable and reliable power source. A power interruption during the update can potentially damage your system and render it unusable.
3. Compatibility
Double-check that the firmware update you’re about to install is compatible with your specific motherboard model and version. Use the manufacturer’s website to verify compatibility before downloading an update. Upgrading to the wrong firmware can cause serious issues, including system instability and boot failures.
4. Read the Instructions
Pay close attention to the instructions provided by the manufacturer. The update process may vary slightly between different motherboard models. Carefully read and follow the specific instructions and warning messages to ensure a smooth and successful update.
Updating the BIOS or UEFI Firmware
Once you’ve found the right update and taken the necessary precautions, you can proceed with the update process. The steps typically involve:
1. Downloading the Update
Download the firmware update file from the manufacturer’s website. The file will usually be in a specific format like an .exe, .bin, or .rom file. Store the downloaded file in a safe and accessible location.
2. Preparing for Update
Depending on the update method, you may need to prepare a bootable USB drive. Some manufacturers provide tools to create a bootable USB drive containing the firmware update. Follow the provided instructions carefully. Otherwise, the BIOS or UEFI setup utility might guide you through the process.
3. Entering the BIOS/UEFI Setup
- Restart your computer and access the BIOS or UEFI setup utility using the designated key.
4. Navigating to the Update Section
- Locate the “BIOS Update,” “Firmware Update,” or “Flash BIOS” option within the BIOS or UEFI setup utility.
5. Selecting the Update File
- In the update section, choose the “Flash from File,” “Update from Drive,” or similar option.
- Select the firmware update file you downloaded earlier.
6. Confirm and Start the Update
- Carefully review the installation process and follow the on-screen instructions.
- Confirm that you want to proceed with the installation.
- The BIOS or UEFI update process may take several minutes to complete.
7. Rebooting the System and Verifying the Update
- After the update is installed, the system will typically reboot automatically.
- Once the computer boots up, you can check the system information to confirm that the firmware update has been successfully applied.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While updating BIOS or UEFI is generally safe, unforeseen problems can occur. Here are some common issues and troubleshooting tips:
- Failed update: If the update process fails or your computer doesn’t boot correctly afterwards, try resetting the CMOS settings (clear CMOS) by removing the CMOS battery on your motherboard for a few minutes.
- Boot errors: If you encounter a boot error after updating, try booting from a different device (like a USB drive with a bootable operating system) and attempting to repair the boot configuration.
- System instability: If you experience system instability after the update, try reverting to the previous BIOS/UEFI version (if available).
3.1.2.5 Lab – Search For Bios Or Uefi Firmware Updates
Conclusion
Updating your BIOS or UEFI firmware can significantly enhance your computer’s performance, security, and compatibility. By following the steps outlined in this lab, you can confidently navigate the update process and ensure that your computer is running at its best. Remember to always prioritize data backups, study the manufacturer’s instructions, and proceed with caution. Keep your computer up to date, and enjoy the benefits of a smooth and secure computing experience!



![Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF] Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF]](https://i3.wp.com/i.ebayimg.com/images/g/2OEAAOSwxehiulu5/s-l1600.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)

