Imagine standing before a majestic mountain range, its snow-capped peaks reaching for the sky. Would you be content with just one perspective – perhaps the front view – or would you yearn to explore its entirety, to understand its form from all angles? Just like that mountain, everything around us – from objects in our everyday lives to the vast expanse of the universe – has multiple dimensions. And understanding those dimensions requires us to embrace the power of different views: front view, side view, and top view.
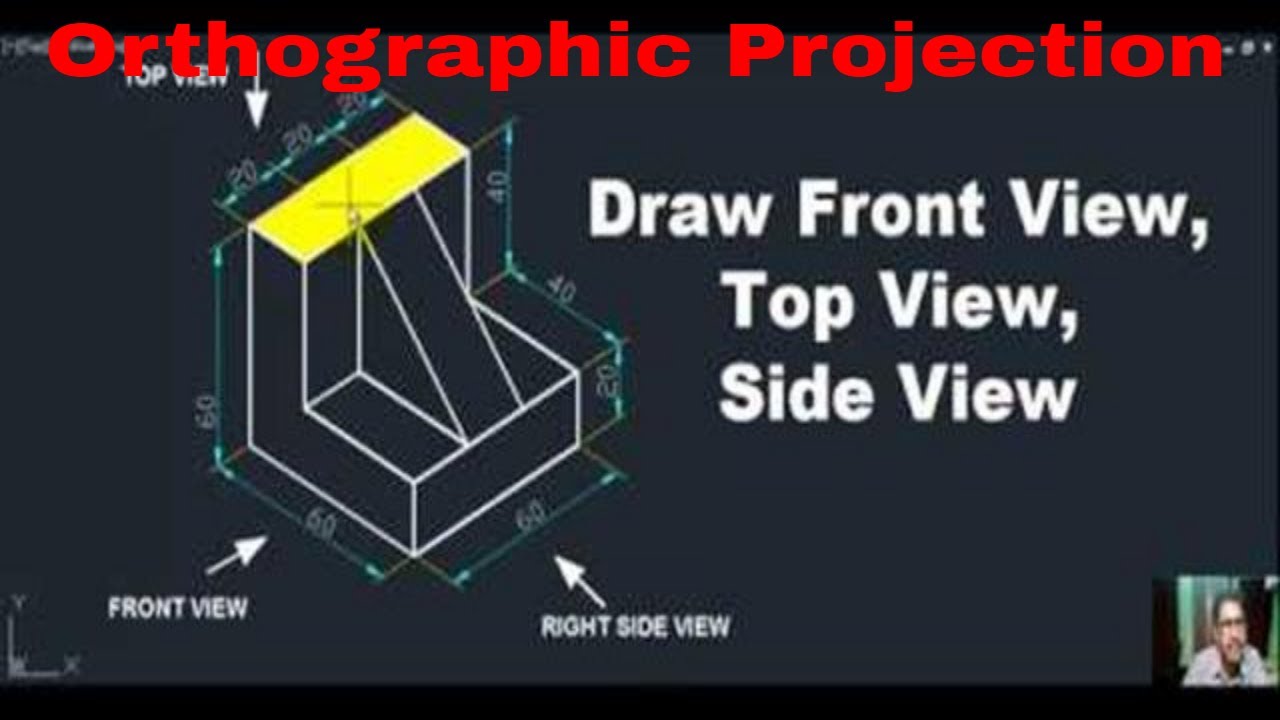
Image: dbdalrymplemicrurus.z21.web.core.windows.net
These seemingly simple terms hold the key to unlocking a deeper comprehension of the world around us. Whether you’re a budding artist, a student of architecture, or simply someone curious about how things work, the ability to visualize objects from different perspectives is invaluable. This article will delve into the significance of front view, side view, and top view, exploring their applications across various fields and empowering you to see the world through a new lens.
A World of Perspectives: Understanding the Basics
At its core, understanding front view, side view, and top view boils down to visualizing an object from different vantage points. Picture a simple cube. The front view captures the face directly facing you, while the side view reveals the profile, and the top view presents an overhead perspective. This basic understanding forms the foundation for numerous disciplines, from engineering to art.
Front View: A Direct Encounter
The front view showcases the object as if you’re standing directly in front of it. Think of a photograph taken face-on – you see the object in its most straightforward presentation. In design, the front view often plays a crucial role in conveying the object’s primary function and overall aesthetic appeal. For instance, the front view of a car would reveal its headlights, grille, and overall design elements, while the front view of a building would showcase its main entrance and architectural details.
Side View: Exploring the Profile
The side view offers a profile perspective, revealing the object’s form from the side. This view enables us to understand the object’s depth, its curves, and its overall silhouette. Imagine looking at a tall skyscraper from its side. The side view reveals its height, its windows, and the subtle curves of its exterior. In art, side views are often used to capture the graceful flow of a figure’s body or the elegant sweep of a landscape.
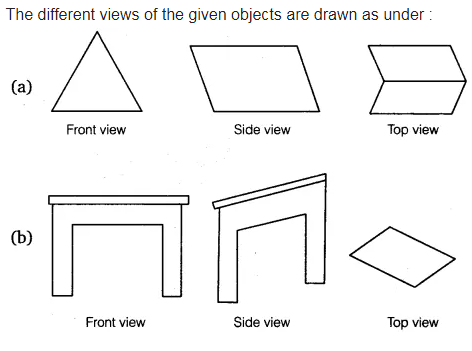
Image: ask.learncbse.in
Top View: A Bird’s Eye Perspective
The top view provides an aerial perspective, as if you were looking straight down at the object from above. This view reveals the object’s plan, its layout, and its spatial relationships. Imagine seeing a city from a plane – the top view allows you to grasp the city’s grid system, its parks, and the overall arrangement of buildings. In architectural design, top views are essential for understanding the floor plan, the placement of rooms, and the flow of movement throughout a space.
Applications Across Fields: A Multifaceted Tool
Beyond the realm of basic geometry, front view, side view, and top view are fundamental tools across numerous disciplines.
Engineering: Building the Future
Engineers utilize front view, side view, and top view to create detailed technical drawings, providing architects and construction teams with precise blueprints for building structures. From bridges and skyscrapers to intricate machinery and complex electronics, these views are vital for visualizing the object’s form and ensuring accurate construction.
Architecture: Shaping the Built Environment
Architects rely heavily on front view, side view, and top view to conceptualize, design, and communicate their ideas. Their sketches and architectural drawings provide a comprehensive understanding of the building’s exterior and interior, its spatial organization, and its interaction with its surroundings.
Art: Capturing the World in Perspective
Artists, from painters to sculptors, employ front view, side view, and top view to create compelling compositions. By manipulating these perspectives, artists can evoke a sense of depth, create illusions of space, and guide the viewer’s eye through the artwork.
Medical Imaging: Peeking Inside the Human Body
In the medical field, front view, side view, and top view are employed in medical imaging techniques like X-rays and CT scans. These views help medical professionals diagnose injuries, identify abnormalities, and understand the inner workings of the human body.
Beyond the Basics: A Deeper Exploration
While front view, side view, and top view serve as foundational tools, there are numerous variations and extensions of these concepts.
Isometric View: A Balanced Perspective
Isometric view is a popular technique in technical drawing, offering a 3-dimensional perspective while maintaining parallel lines. This view combines elements of front, side, and top views, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the object’s spatial relationships.
Perspective Drawing: Capturing Realism
Perspective drawing builds upon the principles of front view, side view, and top view to create realistic depictions of objects and scenes. Using techniques like one-point and two-point perspective, artists convey depth and create illusions of distance, making the artwork appear three-dimensional.
3D Modeling: The Digital Revolution
With the advent of computer technology, front view, side view, and top view have taken on new forms. 3D modeling software allows designers and artists to create digital objects, using these perspectives to manipulate and refine their creations.
Expert Insights and Actionable Tips: Empowering Your Perspective
Understanding front view, side view, and top view is a valuable skill for anyone, but how can you enhance this knowledge and apply it in your own life?
Expert Advice: Embrace the Power of Visualization
“Visualization is a powerful tool, but it takes practice. Start with simple objects, sketch them from different perspectives, and gradually move on to more complex subjects.” – Dr. Amy Carter, Professor of Design at the University of California, Berkeley
Actionable Tips for Enhancing Your Perspective
-
Practice: Draw simple objects from different angles. Start with a cube, then move onto everyday items like a chair, a table, or a lamp.
-
Observe: Pay attention to how shapes and forms change from different vantage points. Observe how light and shadow play on objects based on their position.
-
Explore: Visit museums and art galleries to appreciate how artists use perspective to create compelling compositions.
-
Learn: Take an online course or attend workshops on perspective drawing or technical drawing.
Front View Side View Top View
Conclusion: A Window to the World
Front view, side view, and top view—these simple terms unlock a deeper understanding of the world around us. Whether you’re an artist, an engineer, or simply someone who enjoys observing the world around them, mastering these concepts empowers you to see beyond the surface and appreciate the intricacies of form and space. So, embrace the power of perspective, and let every object, every landscape, and every experience reveal itself in its full glory.



![Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF] Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF]](https://i3.wp.com/i.ebayimg.com/images/g/2OEAAOSwxehiulu5/s-l1600.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)

