Imagine a scene: a massive construction crane, its towering arm poised against the azure sky, and beneath it, a hefty box, nestled securely on the ground. Both are still, frozen in a moment of perfect quietude. But this moment of stillness is far from static. It is a point of equilibrium, a delicate balance of forces, a pregnant pause before the symphony of motion begins. This is the world of physics, where even the act of “resting” is governed by intricate laws and principles.

Image: encarguelo.com
This article delves into the fascinating world of objects at rest, focusing specifically on the scenario of a crane and a box. We’ll explore the forces acting on these objects, delve into the concept of static equilibrium, and even discuss the factors that can tip the scales, leading to a transition from rest to motion. So, join us as we unravel the hidden physics of this seemingly simple, yet powerful, moment of stillness.
Forces in Play: A Balancing Act
Let’s start with the basics. Every object in the universe is subject to forces, whether visible or invisible. These forces can push, pull, or twist, ultimately dictating the object’s motion or lack thereof. Our crane and box are no exception. Here are the key forces at play:
1. Gravity: An Unseen Force
The most obvious force acting on both the crane and the box is gravity. This force pulls everything towards the center of the Earth and is constantly at work. The weight of the crane, with its massive structure and intricate machinery, is a testament to the relentless pull of gravity. Similarly, the box, though smaller, experiences its own gravitational force, pulling it firmly towards the ground.
2. Normal Force: The Counterbalance
While gravity pulls downward, the ground counteracts this force with an upward push known as the normal force. This force acts perpendicular to the surface of contact. In our scenario, the ground exerts a normal force on the box, preventing it from sinking into the earth. The crane, anchored firmly to the ground, also experiences a normal force, providing the necessary support for its massive structure.
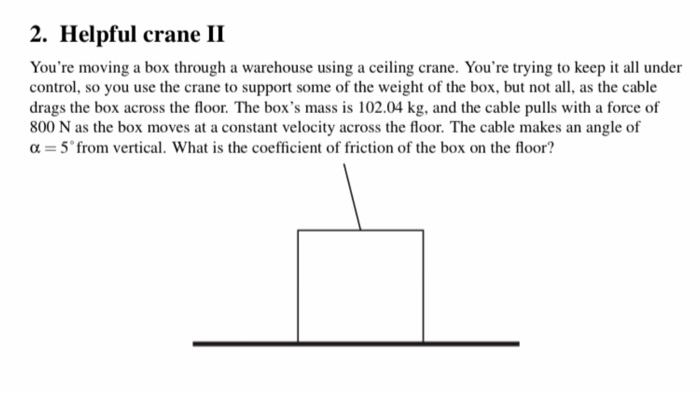
Image: www.chegg.com
3. Tension: The Crane’s Strength
The crane, a marvel of engineering, plays a crucial role in our scenario. The crane cable connecting it to the box exerts a force known as tension. This pulling force is vital for lifting the box. While the box is at rest, the tension force perfectly balances the force of gravity acting on the box, creating a state of equilibrium.
Static Equilibrium: A State of Balance
In our scenario, the crane and box are initially at rest. This state of stillness is not a random occurrence but rather a careful balance of forces. This is known as static equilibrium. When an object is in static equilibrium, it remains motionless because the sum of all forces acting on it is zero. In simpler terms, the forces acting on the object are perfectly balanced, resulting in no net force.
For our resting box, this means that the weight of the box (due to gravity) is perfectly balanced by the upward force of tension in the crane cable. The crane itself is also in static equilibrium, with the normal force from the ground balancing the weight of the crane.
Factors Affecting Static Equilibrium
While our crane and box are initially at rest, this equilibrium is delicate and can easily be disrupted. There are several factors that can upset this balance, leading to motion. Here are a few key factors:
1. Changes in Force
If the tension in the crane cable were to increase, for example, the upward force on the box would become greater than the downward force of gravity. This imbalance would cause the box to accelerate upwards, leaving its resting state. Conversely, reducing the cable tension would lead the box to accelerate downwards.
2. External Forces
External forces, such as a strong wind gust, can also affect the equilibrium. For a box at rest, a powerful gust could push the box, upsetting the balance between the tension force and gravity, causing the box to move.
3. Movement of the Crane
Even the crane, seemingly stationary, can influence the equilibrium. If the crane were to begin rotating, the tension force on the box would change direction, no longer perfectly counteracting the force of gravity. This would lead the box to swing and eventually move away from its initial resting point.
From Rest to Motion: The Shift in Equilibrium
The transition from rest to motion is a fascinating process governed by the laws of physics. This transition marks the disruption of static equilibrium. Here’s how it unfolds:
1. Breaking the Balance
The equilibrium can be broken by a change in forces, introduction of an external force, or movement of the crane. This disruption of the balanced forces leads to a net force acting on the box, causing it to accelerate.
2. Acceleration and Motion
Once the balance is broken, the net force causes the box to accelerate. Acceleration is the rate of change in velocity, meaning that the box begins to move and its speed increases. The direction of acceleration is determined by the direction of the net force.
3. Continuous Motion
As long as the net force is present, the box will continue to accelerate, gaining speed over time. This motion will persist until the net force is removed or until a new force comes into play to counter the movement.
Real-World Applications
The physics of rest and motion are fundamental concepts that underpin numerous real-world applications. Here are a few examples:
1. Building and Construction
Construction cranes, as explored in our scenario, are integral tools in building skyscrapers, bridges, and other complex structures. Understanding the forces acting on the crane and load is crucial for ensuring a safe and efficient construction process.
2. Transportation
Vehicles, from cars to airplanes, experience a complex interplay of forces during motion. Understanding these forces is crucial for achieving optimal performance, safety, and fuel efficiency.
3. Medical Devices
Medical devices like prosthetic limbs and surgical robots rely heavily on the principles of motion and forces. The ability to precisely control movement and understand the interactions between the device and the human body is essential for these technologies’ success.
A Crane And Box Are Both Initially At Rest
https://youtube.com/watch?v=AV_IEisXxV4
Conclusion: The Significance of Rest
While the state of rest might appear unremarkable, it is a fascinating subject of study in physics. Understanding the forces that govern rest, the conditions required for equilibrium, and how this equilibrium can be disrupted are key to understanding the world around us. From the simple act of lifting a box to complex engineering projects, the concepts we explored are fundamental to every aspect of our lives. So, the next time you see a crane and a box at rest, remember that this seemingly simple moment is a testament to the intricate balance of forces and the fascinating world of physics.



![Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF] Cyclomancy – The Secret of Psychic Power Control [PDF]](https://i3.wp.com/i.ebayimg.com/images/g/2OEAAOSwxehiulu5/s-l1600.jpg?w=740&resize=740,414&ssl=1)

